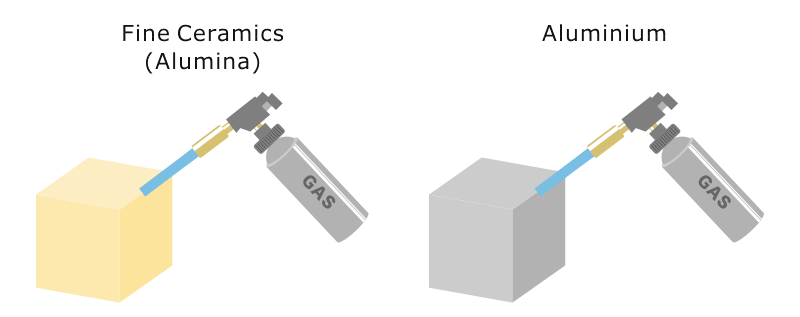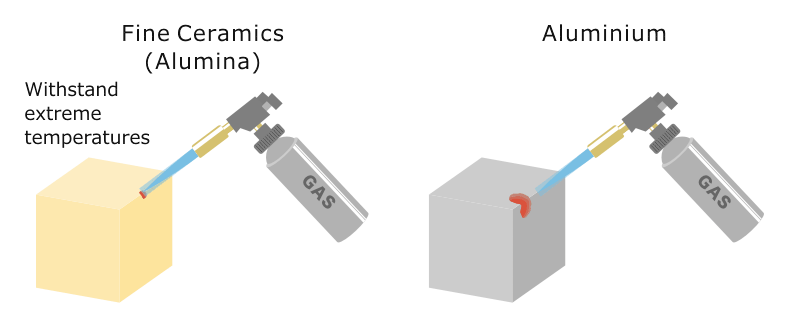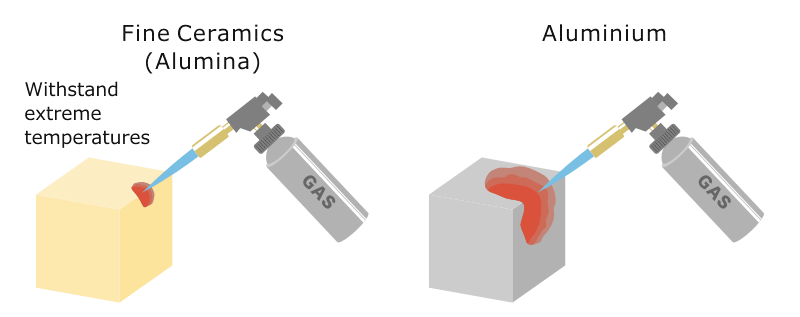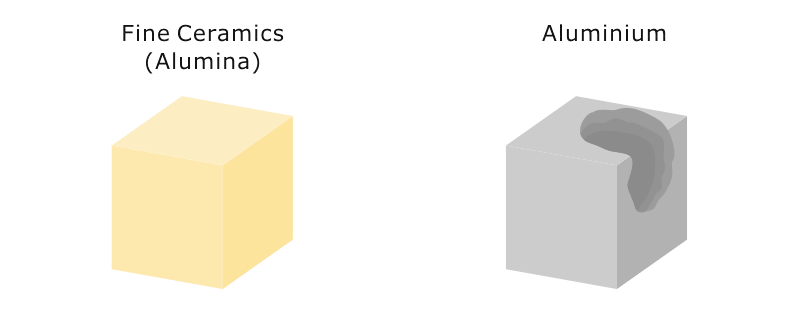
Sustained High Temperature In Ceramics

9 heat flux temperature.
Sustained high temperature in ceramics. Bloating is when ceramics turn to rice bubbles like in expanded clay balls used in aquaponics and hydroponics and may o. 1 extreme environments could be considered as being encountered in applications including handling of molten metals and electrodes for electric arc furnaces but this article will focus on materials being examined for. Ultra high temperature ceramics uhtcs are a class of materials that can be used in environments that exhibit extremes in temperature chemical reactivity erosive attack etc. Temperatures around 600 c.
Ultra high temperature ceramics uhtcs are a class of refractory ceramics that offer excellent stability at temperatures exceeding 2000 c being investigated as possible thermal protection system tps materials coatings for materials subjected to high temperatures and bulk materials for heating elements. Alumina al 2 o 3 is the most popular ceramic substrate while aluminum nitride aln is employed for special applications where high thermal conductivity is necessary. The coated steel in general shows much better oxidation and hot corrosion resistance than the uncoated steel specially at higher temperatures. High temperature oxidation and hot corrosion behaviour of some ceramic based coatings e g.
Topics include both short term behavior strength fracture toughness and r curve behavior and long term behavior creep creep fatigue delayed failure and. Ultra high temperature ceramics uhtcs are candidates for use in sharp leading edge applications. Water can dissolve or deform ceramics that have been low fired i e. Afrl considered uhtcs for long life man rated turbine engines.
During late 1990s nasa ames revived. However an increase in the junction temperature up to 250 c at which sic based power devices work causes serious reliability issues for dbc substrates. Journal of the american ceramic society. Ceramic fired in high temperatures may also be susceptible to water if their mineral particles are soluble in water for example gypsum or calcite.
For temperatures below 1300 1400 c 2372 2552 f crack growth is the key issue in non oxide ceramics particularly sintered and chemical vapor deposited sic that are. Exposure to temperatures that are sufficient to cause bloating melting or vaporization can change it s form. Gap in sustained development during 1980s and most of 1990s. Excellent mechanical property retention was observed up to 1200 c with.
Broadly speaking uhtcs are borides carbides nitrides and oxides of early. Active cooling semi passive heat pipe passive. Examples are the effects of oxidation in the high temperature creep and fracture of βsi 3 n 4 ceramics and the effects of oxidation on crack growth in sintered sic. Effect of sustained high temperature exposure on the mechanical properties of nicalon al 2 o 3 composites.
Borate silicate chromate and carbide oxide on mild steel has been investigated in the temperature range of 400 850 c.