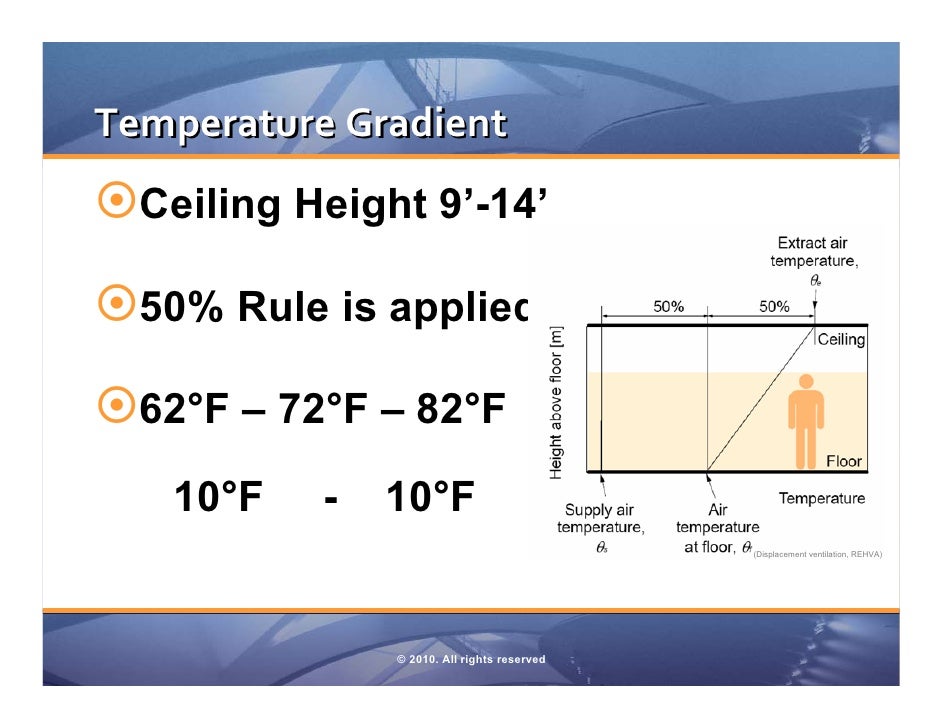
Temperature Gradient From Floor To Ceiling

Applying the temperature gradient calculation to the uninsulated ceiling construction predicts a ceiling cavity temperature of 66 f on a design day 70 f indoors 0 f outdoors.
Temperature gradient from floor to ceiling. The space are small. With equal temperature boundaries. When warm air is introduced with a ceiling diffuser some stratification can be expected due to the lower density of the warm supply air see temperature gradient curve in figure 2. If draft stripping is poor conditions are perfect for a chimney draft to develop in which warm air at ground level is sucked upwards and lost through leaky upper floor windows a.
31 50 33 36 70 0 66 1 f. This variation in room air temperature from floor to ceiling is known as stratification. The air on the ceiling will be the temperature of the ceiling. Stairwells are particularly prone to developing a steep temperature gradient because the ceiling height is at least doubled.
Radiation cross couples all surfaces with all air masses. The average mean water temperature of the panels varied between 14 1 26 2 c. See the temperature gradient curve in figure 1. The displacement ventilation airflow rate varied between 4 0 and 9 9 l s m.
2 and the supply air temperature was kept constant at 18 c. 7 b the lower air layer up to 2 m 7 ft high from the floor is the lower air layer extends to 8 m high from the floor which characterised by a steep vertical temperature gradient is thought to be due to a shallow air discharge angle of the whereas in the upper air layer above 2 m the gradient shal ceiling mounted. The temperature sensors are at 2 ft 6 ft 10 ft and 14 ft above the floor. According to the radiant panel association a radiant heated floor normally feels neutral with a surface temperature usually lower than normal body temperature although the overall.
You re using an unapplicable formula in the comment to your question. From 6 ft up to 14 ft its only about 1f. Radiant floor heating produces room temperatures very close to ideal. R value from outdoors to ceiling cavity.
That sets the gradient in the room. The plots below show the temperatures for a cathedral ceiling room. The air in the room is only one part of a matrix of thermal flux paths. The floor walls and ceiling all play a part by setting the boundary conditions.
The results showed that displacement ventilation and chilled ceiling are able to provide a stable thermal stratification and. Normalized air temperature distributions for test cases with heat gains of 800 w air change rate of 3 0 per hour. About 75 f at floor level declining to 68 f at eye level then to 61 f at the ceiling. Please refer to adiabatic process to see when to use this formula.
The difference in temperature from the 2 ft level to the 14 ft level is about 3f.