The Least Effective Intervention For General Pelvic Floor Impairments
All studies were eligible for inclusion if there was at least one arm with a pfmt protocol alone or together with other adjunctive therapies biofeedback electrical.
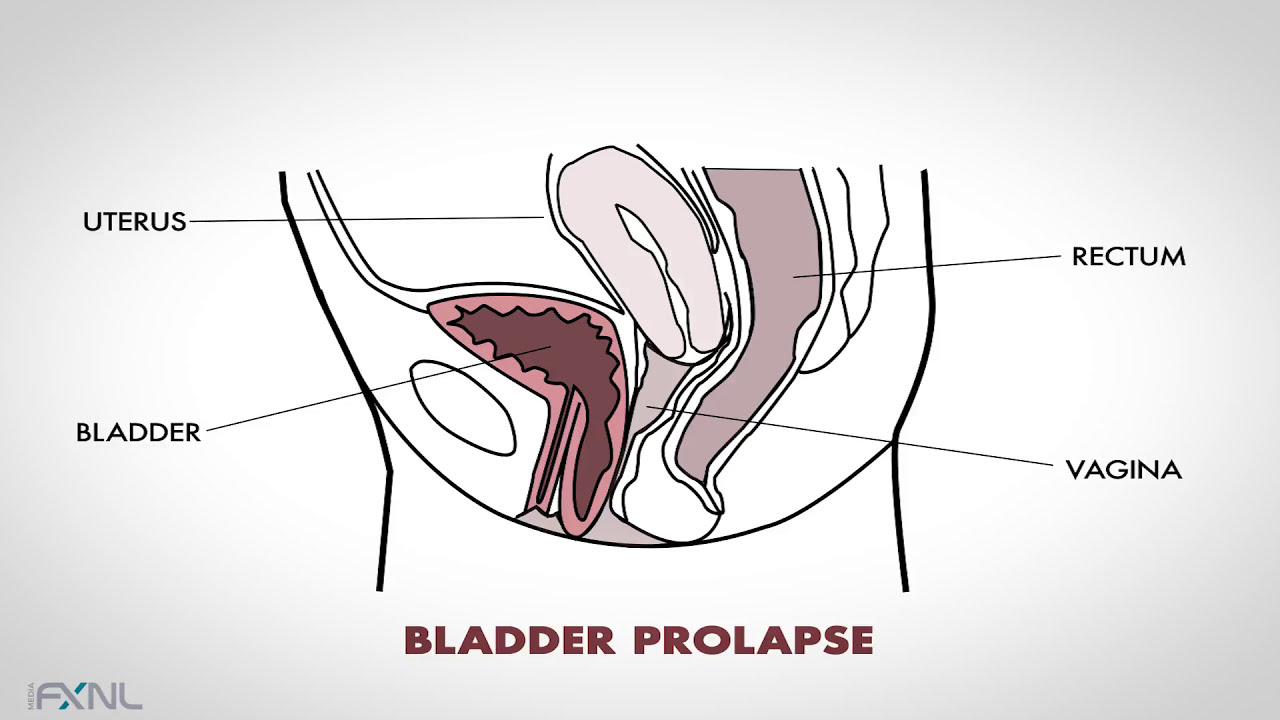
The least effective intervention for general pelvic floor impairments. Stress urinary incontinence sui is defined as the complaint of involuntary urine leakage with physical effort or exertion such as sneezing or coughing. Thirty four patients with gynecological cancers recruited between july 2009 and december 2009 were randomly allocated into two groups. Incontinence urinary and or faecal and pelvic organ prolapse. Pelvic floor intervention strategies for urogenital and breast cancer rehabilitation 1 day webinar course according to the american cancer society more than 14 million americans with a previous cancer diagnosis are living in the united states.
The special issue also raises awareness of the multifaceted approaches that are required when treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Pta s will not be expected to examine and. Types of outcome measures. Electrical stimulation of pelvic floor muscles or other adjunct therapies.
Secondary outcomes were condition specific and general quality of life costs sexual functioning prolapse stage pelvic floor muscle function and women s perceived improvement of symptoms. This month ptj publishes a special issue on rehabilitation for women and men with pelvic floor dysfunction focusing on recent advances in the understanding and management of urinary incontinence pelvic organ prolapse and functional constipation. In women the pelvic floor muscles are put at risk of damage and dysfunction by a series of factors such as high impact exercise obesity pregnancy and childbirth chronic constipation and the menopause. A pfrp group n 17 who participated in a 4 week pfrp exercise program and a non pfrp group n 17 who received the usual health care the pelvic floor strength the motor evoked potentials meps elicited by sacral and transcranial magnetic.
1 behavioral interventions including pelvic floor muscle pfm exercise and functional training in the use of these muscles to prevent urine loss are recommended as first line interventions for sui. A pelvic floor exercises. These have been excluded as they are not normally performed by midwives but rather are part of the physiotherapist s role. B type of instruction of pfme e g.
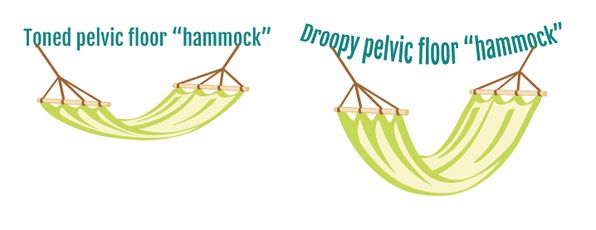
Diagnose impairments of the pelvic floor and surrounding structures and their impact on intervention and function perform an external and internal examination and evaluation of the structures impacted by an underactive pelvic floor rectal and over active pelvic floor vaginal and rectal note. Behavioral therapy resulted in greater patient satisfaction and fewer bothersome incontinence symptoms than pessary at 3 months but differences did not persist to 12 months. Behavioral therapy including pelvic floor muscle training exercise and bladder control strategies. A weakened pelvic floor can have two major negative consequences.